Table of Contents
Introduction
Learn about the classification of nutrients as those that get metabolized and metabolizers. It is a useful way of nutrient classification having several benefits than conventional nutrient classification
There are different ways of classification of nutrients which are mainly carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. I am proposing a new way of classification of nutrients, namely. Nutrients that get metabolism and nutrients that are metabolizers. This will help people understand the nutrients that they should consume, the importance of nutrients, and the role of different nutrients in preventing and reversing diseases.
What are nutrients?
Nutrients are substances that are essential for the body to function properly. They consist of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals, and water. Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are called as macronutrients as they are consumed in large quantities. Vitamins and minerals are called as micronutrients as they are required in small quantities. They provide energy, build and repair tissues, regulate bodily functions, and support the immune system.
The traditional way of classification of nutrients!
Traditionally nutrients are classified as:
- Macronutrients and
- Micronutrients.
Macronutrients: Macronutrients include carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are found in foods such as bread, pasta, rice, fruits, and vegetables.
Fats are also a source of energy. They are found in foods such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, and nuts.
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues. They are found in foods such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, beans, and lentils.
Micronutrients: Micronutrients include vitamins, minerals, and water.
Vitamins are essential for a variety of bodily functions. They help to regulate metabolism, build strong bones and teeth, and protect against disease.
Minerals are also essential for a variety of bodily functions. They help to regulate blood pressure, build strong bones and teeth, and transport oxygen throughout the body.
Water is essential for transporting nutrients throughout the body and for regulating body temperature.
———————————————————————————————————————–
Drawbacks of Classification of nutrients as macronutrients and micronutrients:
- People focus on macronutrients in choosing what to eat and what to avoid. Which carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are good, and which ones are bad for health? They have to decide based on the food item as a whole and not what it actually contains.
- They focus less on micronutrients because they are told that micronutrients are required in very small quantities, and getting that small quantity is not a problem.
- The carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all polymeric in nature and cannot be absorbed in the blood stream. Therefore, which nutrients enter cells cannot be decided at the macro level. What nutrient enters the cells after digestion is important.
All polymeric food items are broken down in the digestive system into simpler units. These nutrients are absorbed from the intestine into the blood stream. From the blood stream, they go to the liver. From the liver, the digested nutrients are distributed to each and every cell in the body.
Thus there is a need for a new method of classification of nutrients based on the nutrients obtained after digestion and the role of those nutrients once they enter the cells.
———————————————————————————————————————–
Nutrients obtained after digestion!
The variety of foods are many but the nutrients obtained after digestion are limited. After digestion about 45 nutrients are obtained from the food.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are digested into glucose, galactose, and fructose. In the liver galactose and fructose are converted to glucose. The main product of the digestion of carbohydrates is glucose plus the vitamins, minerals, and fiber present in the carbohydrates.
Fats: Similarly, fats after digestion give saturated fatty acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and essential fatty acids like linoleic acid (omega-6 fatty acids), and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3 fatty acids), glycerol, and fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, E & K.
Proteins: Similarly, proteins on digestion give 20 amino acids plus vitamins plus minerals. Out of these 20 amino acids, 9 amino acids are essential amino acids. Essential means our body cannot make these amino acids and we have to get them from the food.
Fruits and vegetables: On digestion, we will get fructose, vitamins, and minerals. Fructose is converted to glucose in the liver.
If the food we eat lacks in some of the nutrients, especially vitamins and minerals, then it is called as a poor diet.
TABLE
List of nutrients obtained from food after digestion
| NUTRIENTS | ROLE OF NUTRIENTS |
|---|---|
| Glucose | Source of energy |
| Fatty acids, glycerol, 2 essential fatty acids ( LA & ALA) | Source of energy |
| Amino acids: Alanine, Arginine, Asparagine, Aspartic Acid, Cysteine, Glutamic acid, Glutamine, Glycine, Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Proline, Serine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Valine | Building blocks for muscles, tissues, cells, enzymes, |
| Vitamins Fat soluble vitamins: Vitamin A, D, E & K Water soluble vitamins Vitamin C, vitamin B-1 (thiamine), vitamin B-2 (riboflavin), vitamin B-3 (niacin), vitamin B-5 (pantothenic acid), vitamin B-6, vitamin B-7 (biotin), vitamin B-9 (folate, folic acid), vitamin B-12 (cyanocobalamin) | Vitamins and minerals are essential for a variety of bodily functions, such as immune system support, growth, and development. |
| Minerals magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, sulfur, sodium, potassium, chloride, iron, selenium, zinc, manganese, chromium, copper, iodine, fluoride, molybdenum | Vitamins and minerals are essential for a variety of bodily functions, such as immune system support, growth, and development |
TABLE
List of essential nutrients
| NUTRIENT SOURCE | ROLE OF NUTRIENTS |
|---|---|
| Essential fatty acids | Linoleic acid; Omega-6 fatty acids; LA Alpha linolenic acid; omega-3 fatty acid; ALA |
| 9 essential amino acids | Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Threonine, Valine |
| Vitamins | Vitamin A, D, E & K, Vitamin C, vitamin B-1 (thiamine), vitamin B-2 (riboflavin), vitamin B-3 (niacin), vitamin B-5 (pantothenic acid), vitamin B-6, vitamin B-7 (biotin), vitamin B-9 (folate, folic acid), vitamin B-12 (cyanocobalamin) |
| Minerals | magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, sulfur, sodium, potassium, chloride, iron, selenium, zinc, manganese, chromium, copper, iodine, fluoride, molybdenum |
—————————————————————————————————————————
How nutrients are used by the body?
There are two types of nutrients.
- One, mainly macronutrients, which get converted into energy or some other biological entity.
- The other, mainly micronutrients, which help or offer support in their conversions. Both types of nutrients are essential for good health. Micronutrients are equally important because, without them, things won’t move
Digestion converts foods into its simplest form which can be absorbed in the blood stream and used by the cells to perform their functions. Cells perform several functions. Their performance depends on the nutrients they get. If there is a deficiency of certain nutrients, then the performance of the cells will be affected. This will affect your health.
The nutrients obtained from carbohydrates and fats are mainly used for producing energy. If sometimes your intake of fats and carbohydrates is less, then the body can use amino acids to produce energy.
So, glucose, fatty acids, glycerol, and amino acids are used for producing energy. These are energy-producing nutrients.
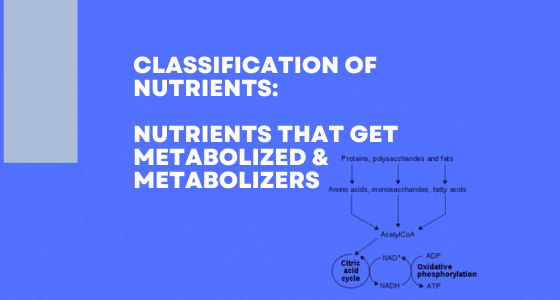
To produce energy these nutrients, undergo metabolism. So we can call them as food or nutrients that get metabolized” or “foods or nutrients that undergo metabolism”. For more details, read the chapter on glucose metabolism.
Amino acids are the main building blocks of the body. They are necessary for producing muscle mass, tissues, and cell repair.
Every day, millions of cells die. Here amino acids are necessary to produce new cells. They are also needed to produce biologically active molecules like enzymes, hormones, etc.
You should not forget to include essential amino acids in your diet. Intake of foods containing essential amino acids and essential fatty acids is very important.
Next comes the micronutrients and fiber. Fiber is not absorbed in the bloodstream and is eliminated from the large intestine. Vitamins and minerals are needed in small quantities because they help, and support in carrying out metabolic reactions, and cell functions without they being used or consumed. They are reused again and again. The most important point is without them the desired functions cannot be carried out. This point is not highlighted, because of which people take it lightly and do not give importance to vitamins and minerals. We can call vitamins and minerals as metabolizers.
—————————————————————————————————————————-
New Way of Classifying Nutrients Based on nutrients obtained after digestion!
There are 2 ways of classification of nutrients based on the nutrients obtained after the digestion of food. They are:
- Nutrients that undergo metabolism: Glucose, fatty acids, glycerol, amino acids. These nutrients are used to produce energy and other biologically important materials like muscle mass, repair tissues, synthesize enzymes, hormones, etc.
- Nutrients that act as Metabolizers: The nutrients which act as metabolizers are vitamins and minerals. The nutrients that undergo metabolism, either anabolic or catabolic reactions, to produce energy from glucose, or fatty acids, and synthesize enzymes or hormones, need these vitamins and minerals as well as specific enzymes present in the body to undergo metabolism. They themselves, without the help of metabolizers, cannot get metabolized. Simple Example: the simple example is the metabolism of glucose in the cells to produce energy. When glucose enters the cell ATP provides energy and converts glucose to glucose phosphate. Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid in the cytosol by anaerobic oxidation. This conversion from glucose to pyruvic acid is a 10-step enzymatic process and each step needs a specific enzyme, a coenzyme, and a cofactor. Coenzymes are mainly made from vitamins and their function is to lower the energy requirement for the enzymatic process. A cofactor is mainly a mineral like magnesium or zinc. If any coenzyme or cofactors is not available, the reaction does not proceed further. Glucose remains there partially metabolized. This affects the cell function and it may die.
——————————————————————————
Benefits of classifying nutrients as metabolizers and ones that get metabolized
It will help you understand why you should not eat sugar and processed foods from which vitamins, minerals, and fiber are removed.
It will help you understand why you should eat more of fruits and vegetables.
It will help you understand that apart from fiber content it is vitamins and minerals that are very essential.
It will help you understand that a deficiency of vitamins and minerals can cause chronic diseases.
It will help you that the functioning of the cells depends on the availability of all the 45 different nutrients obtained after digestion. Better cellular function better the health
It will help you know how you can prevent or reverse diseases just with the help of nutrients. Supplementation may be necessary, especially of water soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B complex vitamins. Vitamin C performs 1000, s of functions in the body.
Conclusion
The new way of classification of nutrients is more helpful than classifying the nutrients broadly as macro and micro nutrients. Nutrients can be classified as nutrients that undergo metabolism and nutrients that act as metabolizers. It gives more and precise information to the people so that they can make the right choice of food.
References
- What are the 6 essential nutrients?: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326132#vitamins
- Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557845/
- ESSENTIAL TO LIFE: Essential Fatty Acids: https://nutritionmeetsfoodscience.com/2020/12/26/essential-to-life-essential-fatty-acids/
- COENZYMES: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/coenzyme